In futures trading, tools that combine both price and volume can offer unique insights into market behavior. One of the most widely used tools among professional and retail traders alike is the Volume Weighted Average Price, or VWAP.
VWAP is more than just another line on a chart. It provides traders with a way to measure where the market has traded on average, adjusted for volume. Because futures contracts are often used for intraday trading, VWAP becomes a valuable tool for understanding where the bulk of activity has occurred.
This article breaks down what VWAP is, how it works, and why it matters in futures trading. We will also cover how to use VWAP strategies, the differences between VWAP and moving averages, and how to apply the VWAP study on MetroTrader.
Key Takeaways
- VWAP stands for Volume Weighted Average Price and accounts for both price and volume.
- Futures traders use VWAP to spot intraday trends, identify fair value, and plan entries and exits.
- VWAP often serves as dynamic support or resistance throughout the trading session.
- VWAP is most effective when combined with other tools, not used on its own.
What is VWAP?
VWAP, or Volume Weighted Average Price, is a technical indicator that shows the average price of a futures contract throughout the day, weighted by trading volume.
Unlike a simple moving average (SMA), which calculates average price based only on closing values, VWAP gives more weight to price levels with higher volume. This makes VWAP a more accurate reflection of the price where most trading activity has occurred.
Traders often see VWAP as a “fair value” line. When price is above VWAP, the market is considered bullish for that session. When price is below VWAP, the market is seen as bearish.
How VWAP is Calculated
VWAP is calculated using the formula:
VWAP = (Cumulative Price × Volume) ÷ Cumulative Volume
Here is how it works in practice:
- Multiply the price of each trade by the volume of that trade.
- Add up these values throughout the session.
- Divide the total by the cumulative trading volume.
For example:
| Time | Price | Volume | Price × Volume | Cumulative Volume | VWAP |
| 9:30 | 100 | 50 | 5,000 | 50 | 100.0 |
| 9:31 | 101 | 100 | 10,100 | 150 | 100.7 |
| 9:32 | 99 | 150 | 14,850 | 300 | 100.6 |
In this simplified table, VWAP is recalculated after each trade. Most trading platforms, including MetroTrader, handle these calculations automatically.
Why VWAP Matters in Futures Trading
VWAP is especially important in futures markets because of their short-term and intraday nature. Here are a few reasons why traders pay close attention to VWAP:
- Fair Value: VWAP highlights the price level where most of the trading has taken place, helping traders understand what institutions may see as fair value.
- Trend Identification: Staying above or below VWAP provides a simple way to read intraday momentum.
- Trade Confirmation: VWAP helps confirm whether a breakout has real strength or is likely to fail.
- Market Efficiency: VWAP is often used as a benchmark for execution quality, especially by institutional traders.
VWAP vs Moving Averages
At first glance, VWAP may look similar to a moving average. However, there are some key differences:
- Resetting Daily: VWAP resets with each new trading session, while moving averages continue across days.
- Volume Weighting: VWAP includes trading volume in its calculation, while simple and exponential moving averages only reflect price.
- Application: VWAP is best for intraday analysis, while moving averages are more flexible for short-term and long-term trends.
For day traders in futures, VWAP often provides a clearer picture of where price is relative to actual market participation.
How Traders Use VWAP in Futures
VWAP has several practical uses in futures trading:
- Intraday Trend Identification: If price trades consistently above VWAP, it signals a bullish session. Below VWAP suggests a bearish session.
- Support and Resistance: VWAP often acts as a magnet, with price revisiting it throughout the day. Many traders treat it as a dynamic support or resistance line.
- Entry and Exit Points: Traders may enter on pullbacks toward VWAP or use it to confirm breakouts.
- Risk Management: Stops and profit targets can be set relative to VWAP, especially for short-term strategies.
VWAP Trading Strategies for Futures
Here are some of the most common ways traders apply VWAP in futures markets:
- Mean Reversion Strategy: Price tends to revert to VWAP during the session. Traders look for overextended moves away from VWAP and trade back toward it.
- Breakout Confirmation: A breakout above resistance is stronger if it also occurs above VWAP. Similarly, breakdowns below support are more reliable when below VWAP.
- VWAP Across Timeframes: Some traders compare the daily VWAP to shorter session-based VWAPs, or use anchored VWAPs for specific market events.
Each of these strategies comes with advantages and risks. Mean reversion can fail in strongly trending markets, while breakout confirmation may deliver false signals in low-volume periods.
Real Scenario: Using VWAP to Trade MES Futures
To see how VWAP works in practice, let’s look at an example with Micro E-mini S&P 500 futures (MES).
Imagine the trading day begins with MES opening above VWAP. During the first hour, price pulls back toward VWAP and tests it as support. At this point, many day traders are watching to see if VWAP will hold.
- Scenario 1: VWAP Support Holds
If MES bounces off VWAP and starts climbing, it confirms bullish intraday momentum. A trader might enter a long position near VWAP with a stop just below it, targeting the previous high of day. - Scenario 2: VWAP Breaks Lower
If MES falls through VWAP with strong volume, that signals bearish pressure. Traders could take short entries, placing stops just above VWAP, and target a move toward the morning session low. - Scenario 3: Choppy Action Around VWAP
Sometimes price chops around VWAP without clear direction. In this case, disciplined traders may avoid entering until a cleaner trend emerges.
This example shows why VWAP matters so much in MES and other equity index futures. Because these contracts are highly liquid, VWAP often acts as a magnet that traders watch closely. It can define risk, confirm breakouts, and guide intraday strategy.
Test VWAP Trading Strategies
Create your MetroTrade account to get a free 30-day trial of MetroTrader
Anchored VWAP in Futures Trading
Anchored VWAP allows traders to start the VWAP calculation from a specific event rather than the start of the trading session.
This approach is useful in futures markets for analyzing reactions to:
- Economic announcements, such as CPI or jobs data.
- Federal Reserve interest rate decisions.
- Contract roll dates when liquidity shifts.
- Major price levels, such as a weekly high or low.
By anchoring VWAP to a meaningful event, traders gain a clearer picture of price relative to that moment.
VWAP in Different Futures Markets
VWAP is not equally useful across all contracts. Its reliability depends heavily on volume and liquidity.
- Equity Index Futures: Highly liquid contracts like the E-mini S&P 500 (ES), Micro E-mini S&P 500 (MES), and Nasdaq (NQ/MNQ) are perfect for VWAP strategies.
- Energy Futures: Crude oil (CL) and natural gas (NG) traders often use VWAP for intraday guidance because of heavy institutional involvement.
- Metals Futures: Gold (GC) and silver (SI) traders apply VWAP to gauge breakout potential.
- Agricultural Futures: Contracts like corn or soybeans are thinner in volume intraday, which can reduce VWAP’s effectiveness, though active traders still apply it.
Common Mistakes When Using VWAP
While VWAP is a powerful tool, traders often make errors in applying it:
- Treating VWAP as a guaranteed support or resistance level.
- Ignoring the larger market trend or key news events.
- Relying only on VWAP without confirming with other indicators.
- Using VWAP in contracts with low liquidity can skew accuracy.
VWAP in Professional and Institutional Futures Trading
Large institutions often benchmark their order execution against VWAP. By doing so, they can measure whether their average price was better or worse than the market average.
This matters for retail traders because price often gravitates around VWAP as institutions execute large orders. Understanding this behavior can help retail traders anticipate where the market may pause or reverse.
Limitations of VWAP in Futures Trading
Despite its strengths, VWAP has limits:
- Short-Term Focus: Because VWAP resets daily, it is less useful for multi-day swing trades.
- Liquidity Dependence: VWAP is less accurate in illiquid markets.
- Not a Standalone Tool: Traders should use VWAP alongside other analysis methods, such as chart patterns, support and resistance, or order flow.
How to Apply the VWAP Study on MetroTrader
MetroTrader makes it simple to apply VWAP on futures charts.
Select the Studies Option on Your Chart
You’ll find it in the top right corner of the chart widget.
Find Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP)
You can scroll through the many available study options or type to search.
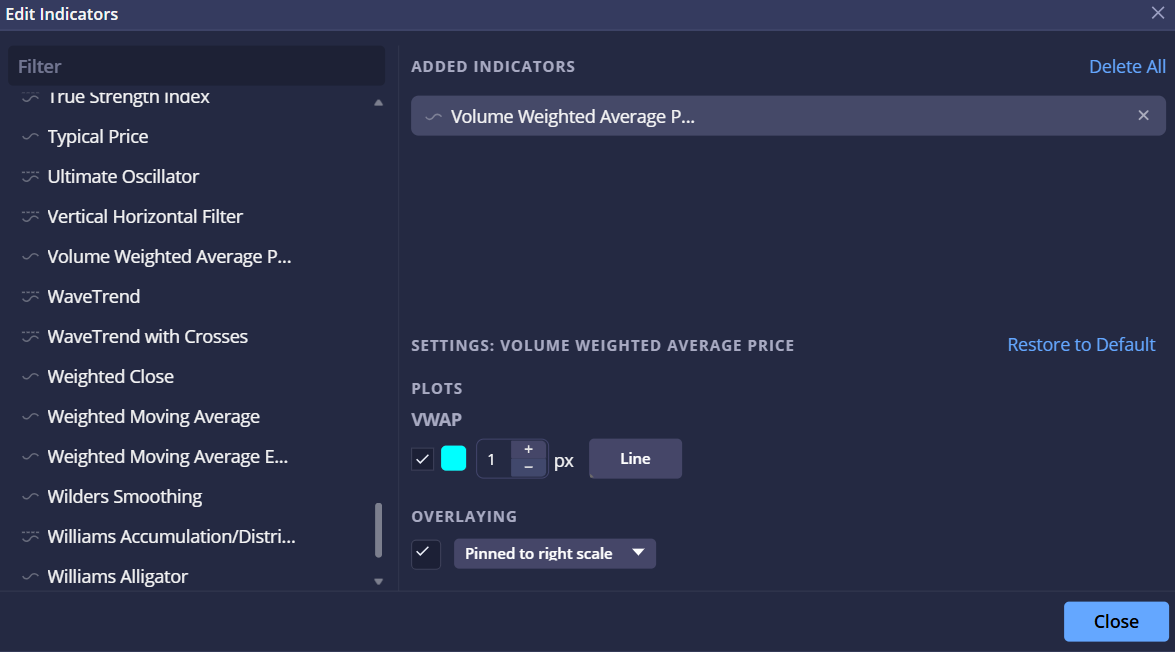
Drag and Drop the Indicator
Simply drag and drop VWAP into the Added Indicators section. It will then automatically apply to the active chart widget.
Conclusion
VWAP is one of the most effective tools for analyzing intraday futures markets. By combining price and volume, it provides traders with an accurate view of fair value and helps confirm whether moves are supported by real activity.
From identifying trends to managing risk, VWAP offers many advantages. At the same time, it should not be used in isolation. Pairing VWAP with other tools and market awareness creates a stronger trading plan.
If you are new to VWAP, the best way to learn is by practicing. Open a MetroTrade account today to explore VWAP and other powerful charting tools before trading live.
FAQs About VWAP for Futures Trading
What is VWAP in futures trading?
VWAP stands for Volume Weighted Average Price. It shows the average price of a futures contract during the trading day, adjusted for volume. Traders use VWAP to find fair value levels and track intraday momentum.
How does VWAP work for futures contracts?
VWAP is calculated by dividing the total of price multiplied by volume by the total volume traded. In futures markets, VWAP updates throughout the day and resets with each new session, giving traders a real-time view of where most activity has occurred.
Is VWAP good for day trading futures?
Yes. VWAP is one of the most popular tools for day trading futures. It helps identify whether the market is bullish or bearish, confirms breakouts, and shows areas where price may act as support or resistance.
What is the difference between VWAP and moving averages in futures?
VWAP resets daily and includes trading volume in its calculation. Moving averages (SMA or EMA) only track price and continue across multiple days. VWAP is better for intraday trading, while moving averages can be used for both short-term and long-term analysis.
Can I use VWAP on all futures markets?
VWAP is most effective in highly liquid contracts such as equity index futures (ES, MES, NQ), energy futures (CL, NG), and metals futures (GC, SI). It is less reliable on thinly traded agricultural or niche contracts where volume is lower.
What is anchored VWAP in futures trading?
Anchored VWAP starts its calculation from a chosen point, such as a news release, contract rollover, or a major swing high or low. This helps traders measure price relative to important market events instead of just the daily session.
How do I add VWAP on MetroTrader?
In MetroTrader, VWAP is available as a built-in study. Open the studies menu, select VWAP, and apply it to your chart. You can customize its appearance and test VWAP strategies in a demo account before trading live.
The content provided is for informational and educational purposes only and should not be considered trading, investment, tax, or legal advice. Futures trading involves substantial risk and is not suitable for every investor. Past performance is not indicative of future results. You should carefully consider whether trading is appropriate for your financial situation. Always consult with a licensed financial professional before making any trading decisions. MetroTrade is not liable for any losses or damages arising from the use of this content.


