Most retail traders follow price action in a single market. But what if you could see when smart money is favoring one market over another before a big move happens?
That’s the idea behind SMT trading in futures. SMT stands for Smart Money Technique or Smart Money Trading. It looks for price divergence between correlated futures markets to uncover hidden strength or weakness. These divergences often show up right before trend shifts or failed breakouts.
Traders use SMT divergence to spot early reversal signals, confirm trades, and avoid traps that catch other retail traders off guard.
In this guide, we’ll break down what SMT trading is, how it works in futures markets, and how you can use it in your own trading strategy. Plus, we’ll cover common mistakes and how to get started with SMT setups using a free demo account on MetroTrade.
Key Takeaways
- SMT trading uses price divergence between related markets to detect hidden strength or weakness.
- Traders commonly apply SMT to correlated futures contracts like ES vs NQ or ZN vs ZB.
- It works best as a confirmation tool, not a standalone signal.
- SMT setups are often used by discretionary and ICT-style traders to identify potential reversals.
What Is SMT Trading?
SMT stands for Smart Money Technique or Smart Money Trading. It’s a concept that focuses on how “smart money” behaves differently from the broader retail crowd.
The core idea is simple: if two markets usually move together, but suddenly start showing different price behavior, that divergence may reveal something important. Smart money may be entering or exiting a position in one market while retail traders chase the other.
SMT trading first gained popularity in the forex world, where traders noticed that currency pairs like EUR/USD and GBP/USD often mirrored each other. But sometimes, one pair would make a higher high while the other would not. That was often a clue that the move was losing strength.
Over time, this concept expanded into futures markets, where the same logic applies to indices, bonds, metals, and more.
How SMT Divergence Works
SMT divergence happens when two related futures markets behave differently at key price levels. For example:
- One market makes a higher high, but the other doesn’t
- One market makes a lower low, but the other holds a support level
- One market breaks out while the other stalls or reverses
This behavior suggests that one market is showing real strength (or weakness), while the other may be faking a move. Traders believe that smart money is often behind the “true” move, and retail traders are usually caught in the fakeout.
The key to SMT divergence is correlation. It only works when the two markets you’re comparing normally move in sync. If they don’t, any difference in price action doesn’t mean much.
Commonly Paired Futures Markets for SMT
Here are some of the most common futures pairs traders use for SMT divergence:
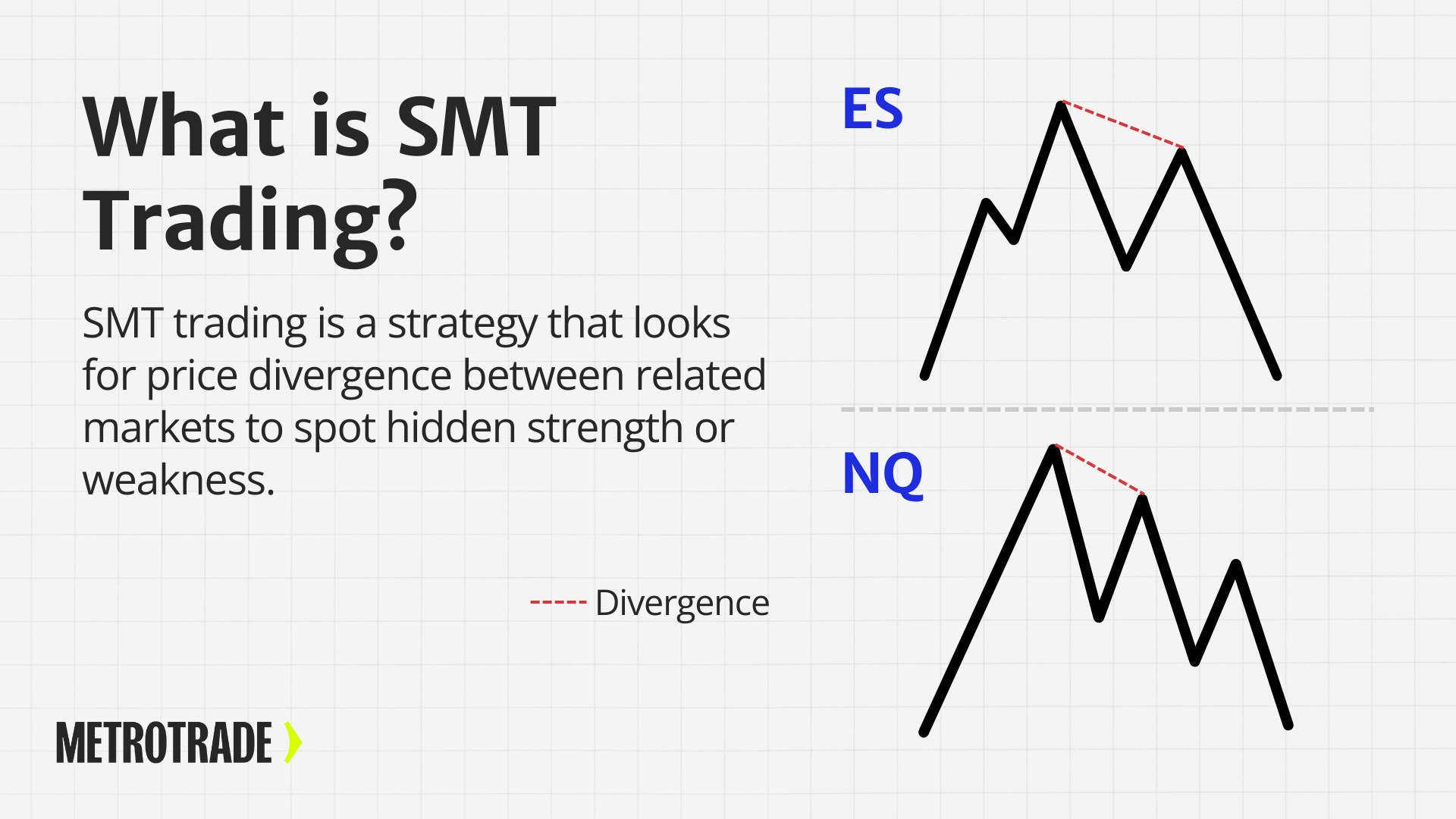
- ES (S&P 500) vs NQ (Nasdaq 100): These two equity index futures are closely linked. SMT setups between them can reveal index strength or tech-sector weakness.
- ZN (10-Year Note) vs ZB (30-Year Bond): Bond traders watch these pairs for divergence in the yield curve or macro shifts in interest rates.
- Gold (GC) vs Silver (SI): Both are precious metals that usually trend together. Divergence often signals strength in one or weakness in the other.
- Crude Oil (CL) vs Brent Oil (BZ): Global energy markets tend to move in sync, but SMT divergence can show changes in supply, demand, or geopolitical pressure.
These comparisons work best on intraday timeframes like the 5-minute, 15-minute, or 1-hour charts, where SMT setups can develop quickly and offer good trade timing.
SMT Trading in Futures Markets
Futures markets are a natural fit for SMT trading because of their liquidity and asset pairings.
When traders apply SMT to futures, they typically look for divergence near key levels, such as:
- Previous day’s high or low
- Session highs and lows
- Fair value gaps or liquidity zones
- Major support or resistance
A typical SMT setup might look like this:
- The ES makes a higher high during the New York open
- At the same time, the NQ fails to make a new high and starts to pull back
- This divergence could signal weakness in the broader move
- A trader might enter a short position with a stop above the ES high
SMT is often used as a confluence in larger systems that include order blocks, market structure, or imbalance zones. It helps confirm whether a move has strength or is likely to reverse.
Real Examples of SMT Divergence in Futures
Let’s walk through some real-world examples of SMT divergence using popular futures contracts:
Example 1: ES vs NQ Divergence at Range High
During the U.S. session, the ES makes a new high above a prior range. At the same time, the NQ fails to break its own high and starts reversing. This signals potential weakness in the rally. Traders watching both markets might see this as a short opportunity.
Example 2: ZN vs ZB Showing Bond Market Shift
The ZN (10-year) makes a higher high during a bond rally, but the ZB (30-year) lags behind. That signals strength in shorter-duration bonds but hesitation in long-term outlook. Macro traders may use this to position for yield curve changes.
Example 3: Gold vs Silver Reversal Setup
Gold breaks to a new high on CPI data, but silver fails to follow. The lack of confirmation from silver suggests gold’s breakout might not hold. Traders could short gold or wait for confirmation before entering long.
These examples are simplified, but they highlight how SMT divergence offers clues that single-market analysis might miss.
How To Use SMT in Your Trading Plan
SMT is not a signal generator by itself. It’s best used as a confirmation tool for traders who already understand price action, support/resistance, and trade setups.
When to Use SMT:
- Near key levels like session highs/lows or liquidity zones
- During high-volume sessions (London or New York open)
- Around news events, where one market may react faster
Entry and Confirmation:
- Wait for divergence to appear at a key level
- Confirm with price rejection, imbalance, or shift in structure
- Set stop losses outside the recent high/low
- Target the opposite end of the range or the next liquidity pool
Risk Management:
- Use SMT to avoid chasing breakouts that don’t have confirmation
- Keep risk small and defined, especially during volatile sessions
- Don’t force divergence where none exists
This strategy is ideal for discretionary traders or those using ICT concepts. It requires focus and the ability to track multiple markets at once.
SMT vs Regular Market Divergence: What’s the Difference?
Many traders are familiar with divergence indicators like RSI or MACD. These tools compare price movement to indicator movement.
SMT, on the other hand, is different. It compares price behavior between two correlated markets, not just one asset and a technical line.
Here’s the key difference:
- RSI/MACD Divergence: Price vs indicator
- SMT Divergence: Price vs price (across two markets)
SMT gives you a market-level perspective. You’re watching how smart money may shift between assets, rather than relying on a lagging indicator.
Mistakes Traders Make with SMT Divergence
Like any trading concept, SMT can be misused. Here are common errors to avoid:
- Using unrelated pairs: Only compare assets that are historically correlated (like ES and NQ). Random pairings won’t give valid signals.
- Forcing divergence: Seeing divergence that isn’t meaningful or significant can lead to poor trades.
- Ignoring context: SMT setups work best near key levels or during volatile periods. Don’t trade them in the middle of a quiet session.
- Skipping confirmation: Just because divergence appears doesn’t mean it’s tradable. Use confirmation tools like price rejection, order blocks, or structure shifts.
SMT works best when it’s part of a bigger plan, not a shortcut to entry.
Tools and Platforms for SMT Trading in Futures
To trade SMT divergence effectively, you’ll need a charting platform that supports:
- Multi-chart layouts or market overlays
- Real-time futures data for multiple contracts
- Clean, fast charts with custom timeframes
On the MetroTrader Web platform, traders can build SMT setups using:
- Side-by-side chart layouts (e.g., ES on one chart, NQ on another)
- Custom timeframes (5m, 15m, 1h) to find intraday divergence
- Full access to CME micro contracts, perfect for small account testing
Whether you’re on desktop or mobile, MetroTrader gives you the tools to watch correlated markets in real-time.
Pros and Cons of SMT Divergence
Pros:
- Helps identify hidden strength or weakness
- Works across asset classes and timeframes
- Offers an edge in reversal setups and range plays
Cons:
- Can be subtle and hard to spot for beginners
- Doesn’t work well in high-correlation markets
- Needs multi-market tracking and clear setups
Use SMT to sharpen your entries and avoid fakeouts, but don’t rely on it alone.
Should You Use SMT in Your Futures Strategy?
SMT is ideal for traders who:
- Already understand price action
- Trade reversals or liquidity setups
- Want a deeper read on market structure
It may not suit traders who:
- Prefer single-market systems
- Rely only on indicators
- Need high win-rate strategies without discretion
The best way to learn SMT is by watching markets in real time, spotting divergence, and tracking how the price reacts after. Over time, you’ll start to see how smart money moves differently from retail flow.
Try SMT Trading on MetroTrader
Want to test SMT divergence in real market conditions?
MetroTrade allows you to trade real CME futures, including micros like MES, MNQ, MGC, and more.
With MetroTrader’s multi-chart layouts and mobile app, you can:
- Track correlated markets side by side
- Test SMT divergence setups in real-time
- Build confidence before going live
Open your account today and start training your eyes for smart money behavior.
Conclusion
SMT trading gives you a different lens on the market. Instead of watching one chart, you watch how related markets move together. That divergence can reveal when smart money is leading, and retail money is lagging.
It’s not a magic trick, and it’s not meant to be used on its own. But as a confirmation tool, SMT can help filter out bad trades and spot high-probability reversals.
Want to test it for yourself?
Open a MetroTrade account and start watching how markets move in pairs. Over time, you’ll sharpen your eye for divergence and start thinking like smart money.
FAQs
What does SMT mean in futures trading?
SMT stands for Smart Money Technique or Smart Money Trading. It looks at price divergence between correlated markets to spot hidden strength or weakness.
How does SMT divergence work?
It works by comparing how two related markets behave near key price levels. If one makes a new high and the other doesn’t, that divergence can reveal market direction.
What are the best futures contracts for SMT trading?
Popular pairs include ES vs NQ, ZN vs ZB, and Gold vs Silver. These contracts are correlated and often show meaningful divergence.
Is SMT a reliable futures strategy?
SMT works best as a confirmation tool within a broader strategy. It’s not a guaranteed signal but offers an edge when used correctly.
Can beginners use SMT trading?
Yes, but it’s better suited for traders who already understand price action and how markets behave around key levels.
What chart setup is best for SMT divergence?
Use a dual-chart layout showing two correlated markets side by side on the same timeframe, such as 5m or 15m.
The content provided is for informational and educational purposes only and should not be considered trading, investment, tax, or legal advice. Futures trading involves substantial risk and is not suitable for every investor. Past performance is not indicative of future results. You should carefully consider whether trading is appropriate for your financial situation. Always consult with a licensed financial professional before making any trading decisions. MetroTrade is not liable for any losses or damages arising from the use of this content.


